Do you know how to avoid DPF problems?
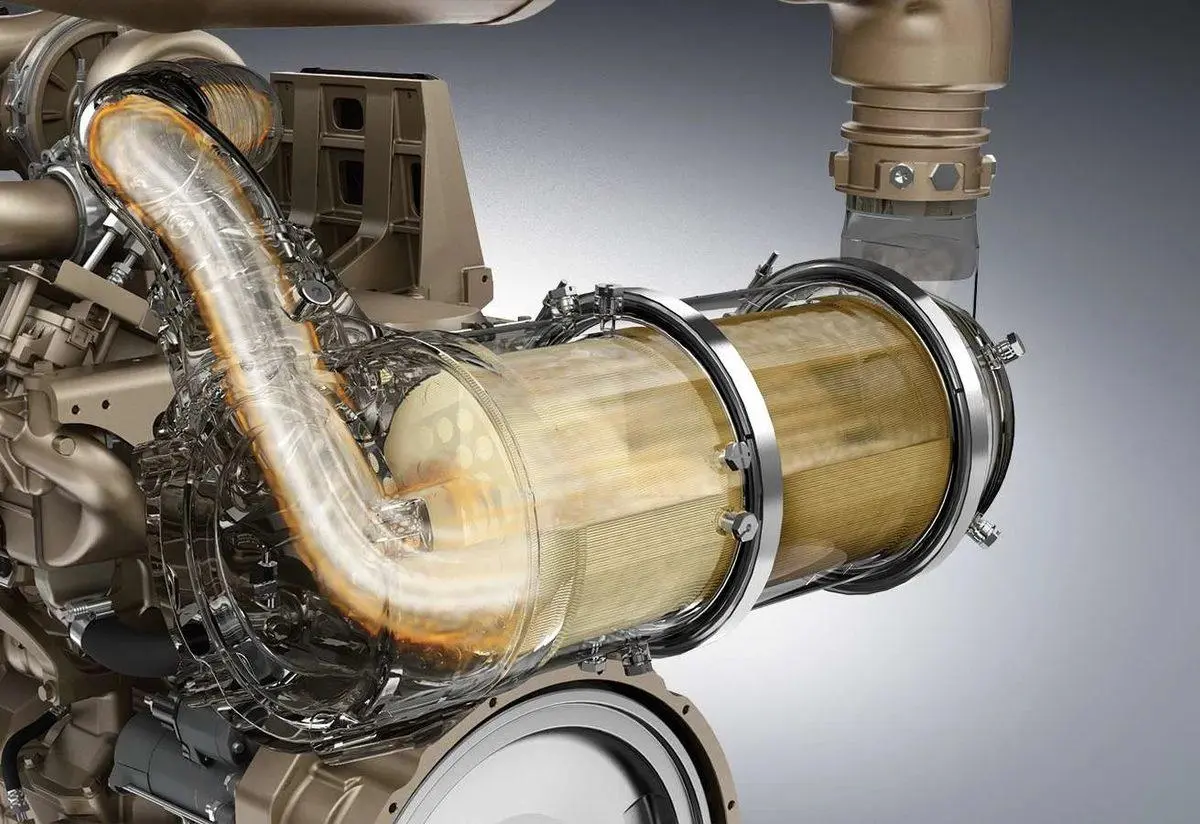
A Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) is designed to capture and trap particulate matter (PM) or soot from the exhaust gases of a diesel engine. The primary purpose of a DPF is to reduce emissions and improve air quality. [1]
Besides unburned fuel, a DPF can catch various components of particulate matter, including:
- Soot Particles: The main target of a DPF is soot, which consists of tiny carbon particles produced during the incomplete combustion of diesel fuel.
- Ash: Over time, ash can accumulate in the DPF. Ash is a non-combustible material that comes from the oil and fuel additives used in the engine. Unlike soot, ash does not burn off during the regeneration process, and it builds up in the filter.
- Metallic Particles: Small metallic particles from engine wear or lubricating oil can be captured by the DPF.
- Silica: Silica particles may come from the combustion of lubricating oil containing silicon-based compounds.
- Other Contaminants: Depending on the operating conditions and fuel quality, a DPF may also capture other contaminants present in the exhaust, such as sulfur compounds and various organic compounds.
Many car manufacturers began implementing diesel particulate filters (DPF) in their vehicles in the mid-2000s as a response to increasingly stringent emissions regulations. Since then, DPF technology has become a standard feature in many diesel cars produced in the last decade.
Every diesel car owner should be aware of DPF issues that may occur, especially on used vehicles with decent milages. It’s fact that quality of new car parts is getting lower and DPF cloggs are not so rare story today.
How to Avoid DPF Problems
Add more fuel
Go for an extended drive. A helpful tip that many people are unaware of is that most cars won’t initiate a regeneration if the fuel level is below approximately one-fourth. This issue can be resolved simply by refueling the gas tank.
The duration and type of driving you engage in should be sufficient to maintain the DPF in good condition. By implementing regular maintenance schedules and using the right fuel, your vehicle’s DPF system will stand a better chance of performing at its best and maintaining its longevity. [2]
Avoid Poor Quality Fuel Use
Selecting the right fuel can play a critical role in maintaining optimal DPF performance. To prevent detrimental DPF issues, it is essential to use a high-quality diesel fuel that meets your vehicle’s specific requirements. This will help to reduce the level of impurities, like ash and metallic compounds, that can accumulate and clog the filter over time.
Here are some tips for ensuring you choose the right fuel:
- Use a premium diesel fuel with lower levels of impurities, as these fuels can help minimize the buildup of particulates.
- Regularly check your vehicle’s fuel filter, as well as the fuel system for early signs of contamination.
- Add appropriate fuel-borne catalyst additives if recommended by the vehicle manufacturer to help with the filter’s regeneration process.
Ensuring Proper Engine Warm-Up
Proper engine warm-up is essential for an active diesel particulate filter (DPF) regeneration process because it helps to ensure that the exhaust temperature reaches the necessary level for efficient regeneration.
During the warm-up phase, the engine and exhaust system reach optimal operating temperatures, which is crucial for the DPF regeneration process to effectively burn off accumulated soot and particulate matter. Inadequate warm-up can lead to insufficient exhaust temperatures, hindering the regeneration process and potentially causing issues with the DPF system.
Therefore, allowing the engine to warm up properly before initiating an active DPF regeneration is important for maintaining the effectiveness and longevity of the DPF system.
Fix underlying issues
Often a DPF issue is actually a symptom of another problem. It means that you have potential problems with the exhaust gas recirculation sensor, turbocharger, fuel injectors, or something else related to combustion and injection.
Avoiding Unnecessary Short Journeys
DPF functions optimally when the engine is running at higher speeds and consistent temperatures, typically achieved during longer journeys or highway driving. In contrast, frequent short trips can contribute to the accumulation of soot in the DPF, increasing the risk of clogging.
To minimize the risk of clogging, consider planning your trips to ensure longer drives. For example, combine multiple errands during a single outing or choose a scenic route that allows you to maintain higher engine speeds and temperatures. Regularly driving for longer durations at steady speed helps to maintain the DPF by allowing passive regeneration to occur. [2]
It is also recommended to avoid rapid acceleration at lower engine speeds, as it can cause unburnt fuel to pass through the exhaust system, forming soot that contributes to DPF clogging.
Don’t drive on low RPMs All The Time
Low RPMs lead to incomplete combustion, insufficient exhaust temperatures, and increased soot accumulation. This can clog the DPF, reduce efficiency, and necessitate more frequent regeneration cycles.
Operating at low RPMs also risks oil dilution, reduces engine performance, and may compromise the overall health of the emissions control system. Varying driving conditions, including occasional higher RPMs, is recommended to maintain optimal DPF function and prevent related issues.
Inadequate Maintenance
Implementing a regular maintenance schedule is crucial for avoiding DPF problems. It helps to keep the vehicle performing optimally and extends the lifespan of its components. Consider the following maintenance practices:
- Periodically clean the DPF through chemical cleaners or manual methods, as proper cleaning helps maintain its efficiency. This should be done once in 6-12 months.
- Regularly check and replace engine oil as per the vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations, ensuring the chosen oil meets DPF-compatible specifications.
- Replace fuel filters at prescribed intervals to prevent contamination that could affect DPF functionality.
- Keep an eye on warning lights and address any DPF-related errors immediately, as ignoring them can lead to bigger issues and costly repairs.
DPF Cleaning Techniques
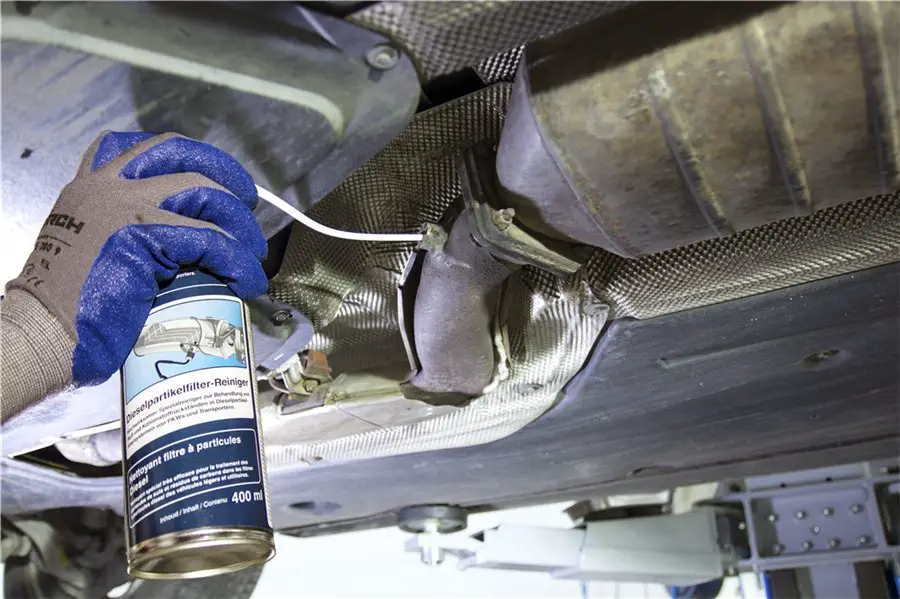

Manual DPF Cleaning
Manual cleaning involves physically removing the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) from your vehicle and following a step-by-step process to clean it. Begin by removing the filter from your car and testing it for any issues. Then, use compressed air to blow out the accumulated soot and ash particles from the filter. Afterward, rinse the filter off with water to remove any remaining residue.
For a more thorough clean, consider using a DPF chemical cleaner specifically designed for this purpose. These cleaners help dissolve stubborn deposits, making them easier to remove. Ensure that you follow the manufacturer’s instructions to achieve the best results.
On-car DPF Cleaning Methods
On-car cleaning methods involve performing a regeneration process, which helps burn off the accumulated soot and particles without removing the DPF from your vehicle. There are two common regeneration techniques:
- Active regeneration: This process is initiated by your car’s engine control module (ECM) when it detects a significant amount of soot buildup. It involves raising the exhaust temperature to a point where the soot can be burned off2.
- Passive regeneration: It occurs during normal driving conditions, especially during long drives at steady speeds3. The process relies on the exhaust temperature being high enough to naturally burn off the soot.
Apart from these methods, you can also use DPF additives to help prevent excessive soot buildup. These additives are added to the fuel and help lower the temperature at which soot is burned off.
This can assist in keeping the DPF clean and maintaining engine performance. Ensure that you choose an additive that’s compatible with your vehicle and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding usage. [3]
In conclusion, both manual and on-car DPF cleaning methods can help maintain your car’s performance and avoid potential DPF problems. Regular cleaning, combined with preventive measures, such as using additives, can help extend the life of your diesel particulate filter and keep your car running smoothly.
When to Seek Professional DPF Services

Recognizing Advanced DPF Issues
Diesel particulate filters (DPFs) play a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions from diesel engines. However, they can cause maintenance problems if not well-maintained. Some common symptoms of clogged or failing DPFs include reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and a check engine light on the dashboard1.
- Reduced Engine Performance: A clogged DPF can cause the engine to lose power due to restricted exhaust flow. This is often accompanied by poor acceleration and overall performance.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: As the DPF becomes clogged, the engine needs to work harder, leading to higher fuel consumption and reduced fuel efficiency.
- Check Engine Light: The vehicle’s onboard computer monitors the DPF’s performance and may trigger the check engine light if it detects issues, such as excessive backpressure.
Consulting with Diesel Specialists
If any of the symptoms mentioned above or trouble codes are observed, it’s important to consult a specialist in diesel engine maintenance. Professional DPF services, like those performed by Throttlebias, can help diagnose and resolve the problem. These experts can provide practical maintenance tips, as well as perform advanced cleaning and replacement processes when necessary. They can also determine whether other components, such as sensors, are causing or contributing to the issue.
An expert in diesel engine service is also equipped to handle the high operating temperatures required to remove particulate matter from the DPF. Keep in mind that the filter must operate at over 400 degrees Celsius to effectively trap and remove particulates.
Monitoring DPF Health

Maintaining the health of your vehicle’s diesel particulate filter (DPF) is crucial in avoiding potential problems. In this section, we will discuss two important approaches: using DPF monitoring tools and interpreting DPF warning signals.
Using DPF Monitoring Tools
There are various tools available to aid in monitoring the health of your DPF. These tools help detect potential issues, allowing you to act early and prevent problems.
- OBD-II Scanners: On-board diagnostic (OBD) scanners are essential tools for diagnosing DPF issues. They can read and clear DPF-related fault codes, as well as display real-time data about your vehicle’s performance. Make sure to choose a scanner compatible with your vehicle and capable of reading DPF-specific codes.
- DPF Regeneration Tools: Some vehicles allow manual regeneration of the DPF using a dedicated tool or by following specific procedures. These tools initiate a forced regeneration, which can help clear out excessive soot and ash buildup.
- DPF Cleaning Kits: Regular cleaning and maintenance of your DPF using a cleaning kit can help prolong its life and prevent issues. These kits usually include a chemical cleaner that can break down soot and ash deposits. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for using the kit.
Read Also: How To Know If Your DPF Has Been Removed
Interpreting DPF Warning Signals
Your vehicle’s DPF warning signals are vital in detecting potential issues. Be on the lookout for these common symptoms, as they may indicate problems with your DPF:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: The check engine light may turn on as a result of an underlying DPF problem. It is important to consult a professional or use an OBD-II scanner to read the codes and determine the specific issue. If the light is flashing, it may indicate a more urgent problem requiring immediate attention.
- Decreased Performance: If your car experiences a decline in performance, including reduced power or acceleration, it is a possible indication of a blocked or malfunctioning DPF. This can be confirmed by analyzing data from an OBD-II scanner or obtaining a professional diagnosis.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A clogged or damaged DPF may lead to increased fuel consumption. This is because the system struggles to process exhaust gases efficiently, requiring more fuel to maintain engine performance.
Related: Problems After DPF Removing
Conclusion
Monitoring DPF health using the appropriate tools and understanding warning signals are essential steps to avoiding DPF-related issues. Regular maintenance and swift action when problems arise will help ensure the longevity of your vehicle’s DPF.
Read Next: How To Choose The Right Exhaust