How can you tell if a DPF has been removed?
If you want to buy a used vehicle, it’s very important to determine if DPF is still there. Buying and running a car without DPF may cause a lot of problems.
Not only you will endanger the environment, but you can be even stopped by police for polluting and excluded from traffic.
The DPF is designed to minimize the hazardous emissions from the car exhaust system by capturing and eliminating particulate matter from exhaust gases.
However, some drivers may remove their DPFs for a variety of reasons. These may include delivering more power and better acceleration or even reselling!
They also intend to reduce exhaust gas temperature, boost fuel economy, and improve throttle response in some cases. Here are quick and easy ways to tell if a diesel vehicle’s DPF has been removed.
How Can You Tell If A DPF Has Been Removed

The best way is to lift the car at some mechanic shop and check if DPF is still there. In some DPF is not located under the car. Another way can be to use OBD2 to check a car for emissions tests. However, extensive black smoke will be the number one proof that DPF has been removed.
- Check with a Piece of Cloth
One quick and easy method to check for the presence of a DPF is by using a piece of cloth. Grab a piece of cloth and place it on your exhaust pipe, then rev the engine. If your vehicle has a DPF, the cloth should remain relatively clean. However, if there is no DPF, the cloth will quickly become covered in black soot.
Alternatively, using your finger is another method to check for a DPF’s presence. Insert your finger into the exhaust pipe, but first ensure the exhaust is not hot. If the DPF is present and functioning correctly, your finger should come out clean. However, if there’s no DPF or it’s malfunctioning, your finger may have black soot stains [1].
It is critically important to remember that such a procedure is only a basic inspection and not an ultimate diagnostic tool. Therefore, consult your owner’s manual or have a professional mechanic evaluate your car for accurate information about your vehicle’s emission control systems.
- Emissions Test Failure
In many areas across the globe, vehicles are required to undergo regular emissions tests. A car without a DPF will likely fail these tests due to the increased particulate emissions. The test involves measuring emissions from the vehicle’s exhaust to assess compliance with emissions regulations with the Ministry of Transport.
An exhaust gas analysis provides additional evidence of DPF removal. During the analysis, a professional measures the levels of pollutants like particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the exhaust [2].
If the analysis shows significantly higher levels of pollutants than expected, it could indicate that the DPF has been removed. Furthermore, a removed DPF may lead to an altered emission profile, with higher emissions during regular driving conditions. This deviation from the expected emission profile can strongly indicate DPF removal [3].
- Using Diagnostic Software
An advanced way to determine whether the DPF has been removed is by utilizing diagnostic software designed for this purpose. Such software provides detailed insights into the status of the DPF and its functionality.
You can use emissions tests and specialized diagnostic software like Rheingold and VCDS.
For example, Rheingold is a diagnostic software tool commonly used for BMW and MINI vehicles. It can be employed to check the pressure within the DPF at various engine RPMs.
In a properly functioning DPF, you should observe varying pressure levels as the engine RPM changes. However, if the pressure consistently reads zero across different RPM ranges, it suggests that the DPF has been removed.
Another common software is VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System), a diagnostic tool primarily used for Volkswagen Group vehicles, including Volkswagen, Audi, SEAT, and Škoda [4].
When using VCDS for DPF analysis, the key parameters to focus on are the ash mass content and soot level.
If the DPF is functioning effectively, these values will typically read more than zero. This is because the DPF collects and stores soot and ash over time.
However, if the DPF has been removed, the ash mass content and soot level will likely register as 0%.
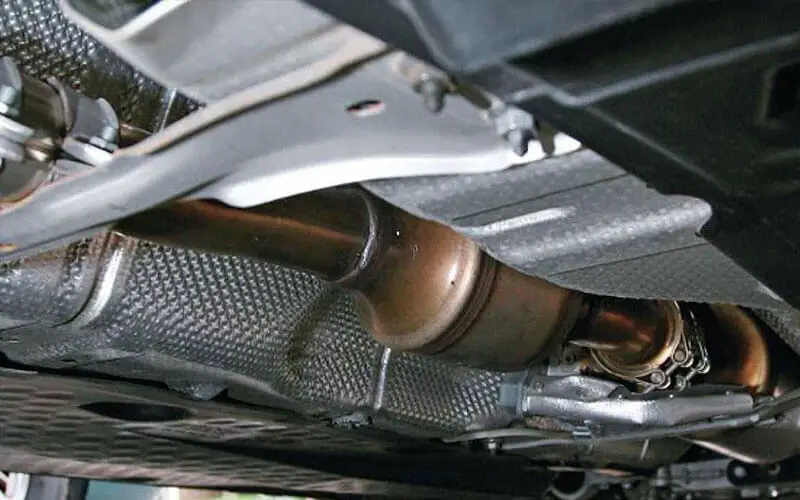
- Run a Physical Inspection
A physical vehicle inspection can also reveal whether or not the DPF has been removed. This entails removing the undertray of your car to see if the DPF has been removed. The DPF is usually located underneath the vehicle in the exhaust system. It is similar to a catalytic converter or a small muffler.
If you notice a straight pipe instead of the DPF, it has most likely been removed. However, some people hollow out the DPF cover and leave it in place, giving the impression that the DPF is still intact.
You should therefore augment your visual assessment with other inspections to verify. Inspect the exhaust pipes for signs of recent welding. Such symptoms show that the DPF has been tampered with or removed.
- OBD-II Scanning
Modern diesel vehicles come with an On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) system that continuously analyses different engine parameters. The parameters include the status of emissions-related components like the DPF. Thus this feature can be used to help check the DPF’s status.
To complete this test, insert the OBD-II scanner into the vehicle’s diagnostic port, which is normally situated beneath the dashboard. Once connected, navigate to the scanner’s menu to check the DPF status.
It should show the DPF’s condition information, such as regeneration frequency and soot load [5]. If the OBD-II scanner indicates that the DPF is missing or that regeneration events are unusually uncommon, it may suggest DPF removal.
Related: How To Avoid DPF Problems
- Turbo Whistle and Diesel Smell
One noticeable auditory indicator that may suggest DPF removal is the presence of a pronounced turbo whistle [6]. When the DPF is removed, exhaust gases flow more freely through the system, increasing the turbo whistle sound.
Pay close attention to the turbo whistle as you accelerate. If you notice a significant increase in the intensity of the whistle, it may suggest that the DPF has been removed.
Moreover, removing the DPF can alter the composition of the exhaust gases, resulting in a change in the odor of the diesel emissions.
When the DPF is removed, unburned particles and different chemical compounds may be present in the exhaust, leading to a distinct change in smell.
Read Next: Problems After DPF Removal
Conclusion
Checking whether DPF has been removed from a diesel vehicle is essential for regulatory compliance and environmental concerns. To ensure that your vehicle is reliable and adequately performing you to have regular maintenance and adherence to emissions regulations.
A thorough review of the vehicle’s maintenance history is an effective method to determine if a DPF has been tampered with or removed. Always exercise caution when considering the purchase of a used diesel vehicle and consult with professionals when in doubt about its emissions system integrity.
Read Next: Mercedes A3 Service